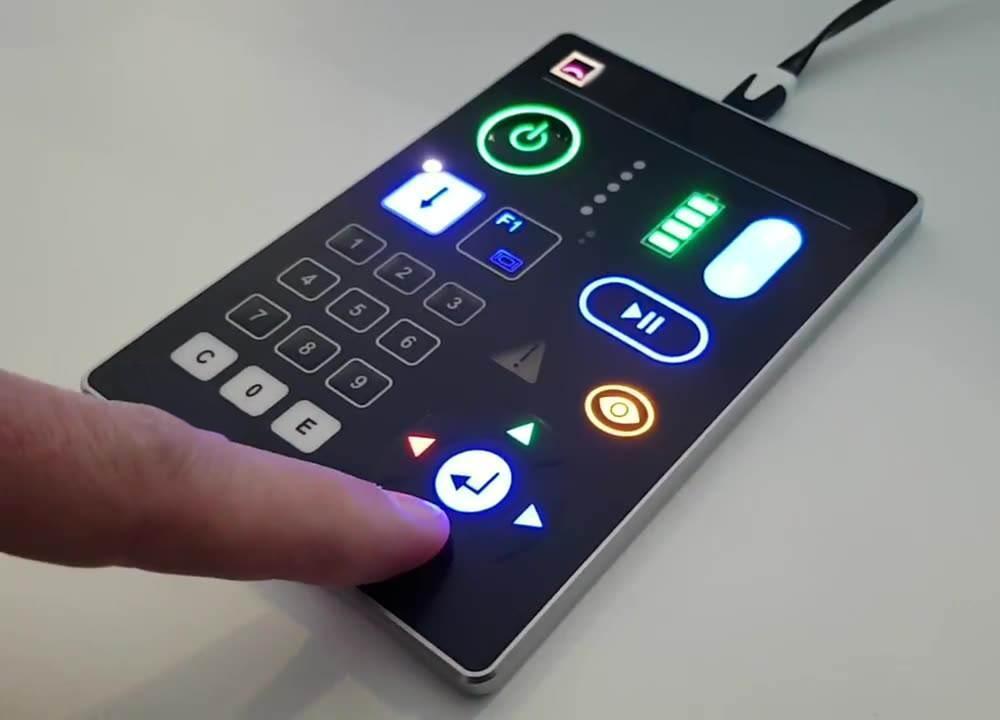
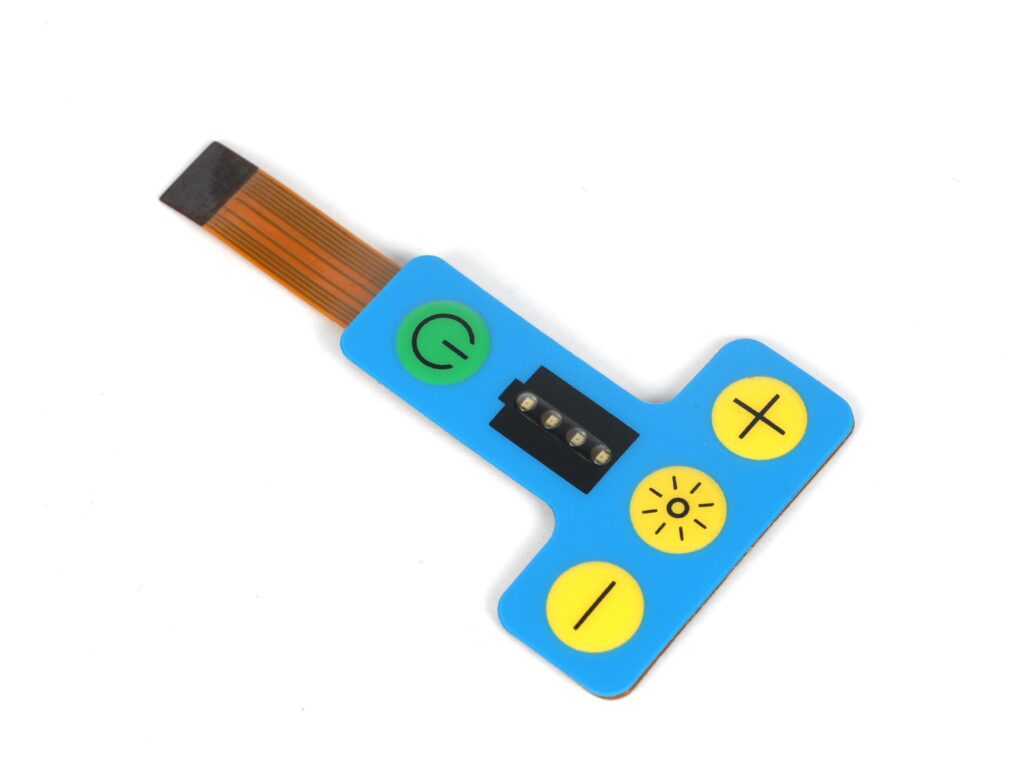
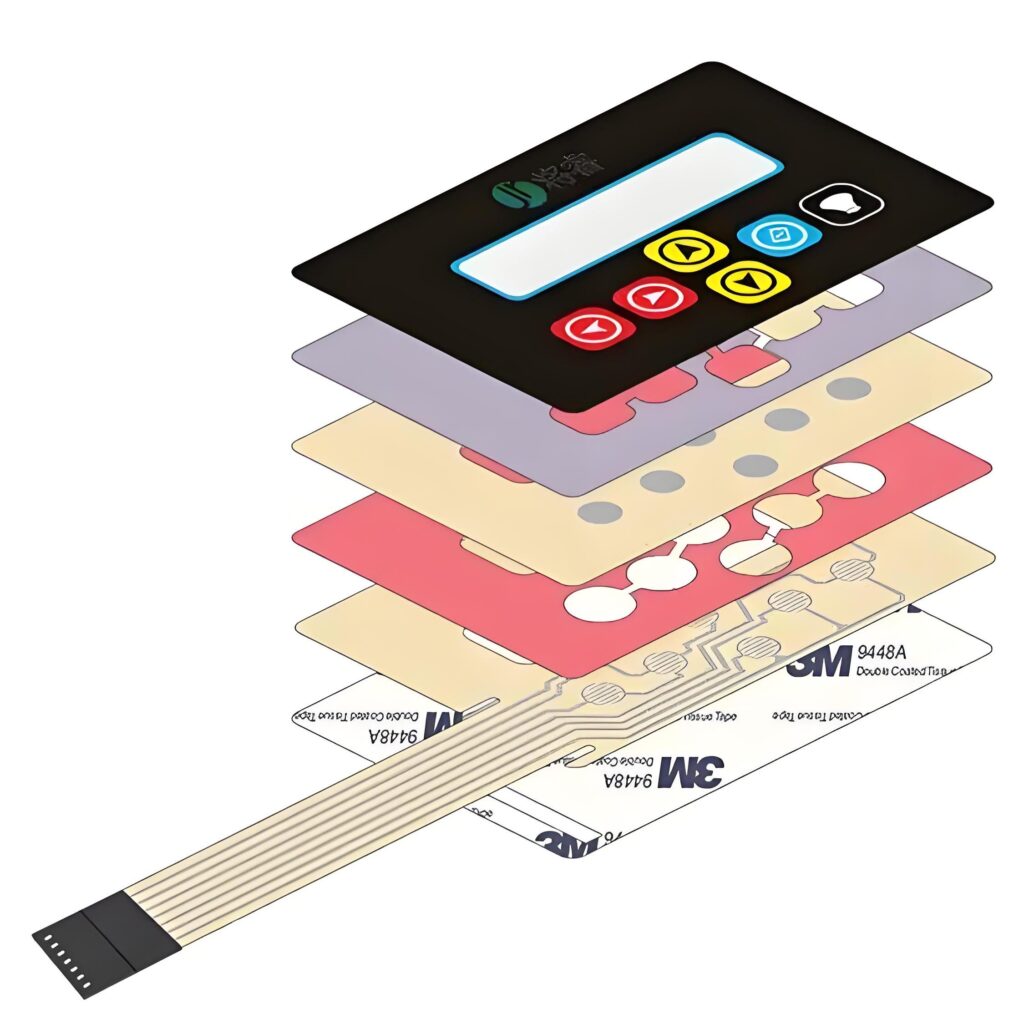
A membrane switch is a new type of electronic switch that integrates key functions, indicating elements, and instrument panels. When a finger presses the mask layer of a membrane switch, the mask layer will deform downward, causing the conductive parts of the upper circuit layer and the lower circuit layer to contact, and the circuit is now turned on.
How does a membrane switch work?
The working principle of a membrane switch is mainly based on its multi-layer structure design. A membrane switch is usually composed of six layers of materials, including a panel, a surface adhesive, an upper circuit, an isolation layer, a lower circuit, and a bottom adhesive.
When the panel is not pressed, the membrane switch is in a normal state, the upper and lower contacts are disconnected, and the isolation layer isolates the upper and lower circuits; when the panel is pressed, the contacts of the upper circuit deform downward, overlap with the lower circuit, and turn on the circuit. The turned-on circuit gives a signal to the external connection instrument (substrate), thereby realizing its corresponding function; when the finger is released, the contacts of the upper circuit rebound, the circuit is disconnected, and the circuit triggers a signal.
What materials are used in membrane switches?
Membrane switches mainly use the following materials:
Polycarbonate (PC): PC film has excellent temperature resistance (-30?~130?), high impact resistance and high elasticity, strong processing adaptability, can be pressed into different textures, and has high insulation strength and non-directionality.
Polyester (PET): PET film has good switch button life and excellent corrosion resistance and wear resistance, and excellent insulation performance. Although the price is slightly higher than the PC panel, its temperature resistance and mechanical properties are also relatively good, suitable for instruments and home appliance panels with higher requirements.
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC): PVC film is cheap, has good chemical corrosion resistance and insulation performance, but poor temperature resistance (about 60?), poor tensile and wear resistance. PVC film is suitable for sign panels, but not suitable for membrane switches and touch panels.
What is an example of a membrane switch?
Examples of membrane switches include rice cookers, washing machines, radiation detectors, and light remote controls. The membrane switches on these devices are usually distributed on the control panel, and the operation function is achieved by the vertical bounce of the elastic membrane.
What are the disadvantages of membrane switches?
The main disadvantages of membrane switches include:
Require physical contact: Membrane switches require physical contact and force to operate, which limits the stiffness and thickness of the coating, the speed of operation, and ease of use.
Limited life: Due to wear caused by physical contact, the life of membrane switches is limited, and their operation may become difficult over time.
Advantages of membrane switches include:
Reliable: Membrane switches have stable and reliable performance and are suitable for various harsh environments.
Dustproof, waterproof, and corrosion-resistant: Membrane switches have good dustproof, waterproof, and corrosion-resistant properties and are suitable for various occasions that require protection.
Lightweight and small size: Membrane switches are light and small in size, making them easy to install and use.
Rich colors and beautiful appearance: Membrane switches are colorful and beautiful, which can enhance the overall aesthetics of the product.
What is the difference between a tactile switch and a membrane switch?
The main differences between tactile switches and membrane switches are their working principles, application scenarios, and user experience.
Working Principle
Tactile switch: Tactile switch uses metal dome button or polymer dome button. When the button is pressed, the contact deforms and contacts the circuit, thus activating the circuit. After releasing the button, the contact rebounds and the circuit is disconnected.
Membrane switch: Membrane switch creates or disconnects the circuit by applying pressure on its surface. When the button is pressed, the contact of the upper circuit deforms and contacts the plate of the lower circuit to conduct. After releasing the button, the contact rebounds and the circuit is disconnected.
Application scenario
Tactile switch: widely used in scenarios that require physical button feedback, such as industrial control panels, medical equipment, instrumentation, etc.
Membrane switch: suitable for occasions with strict space requirements and waterproof and dustproof requirements, such as electronic communication equipment, smart toys, household appliances, etc.
User experience
Tactile switch: provides clear tactile feedback. Users can confirm whether the button is pressed by feel, which is suitable for application scenarios that require intuitive operation feedback.
Membrane switch: usually does not provide tactile feedback, relying on indicator lights or sounds to confirm the operation. This design makes the membrane switch more concise and suitable for occasions that require operation sound.
What is the difference between a membrane switch and a mechanical switch?
There are significant differences between membrane switches and mechanical switches in many aspects:
Lifespan: The working life of a membrane switch is dozens of times that of an ordinary mechanical switch. The life of a membrane switch can reach more than 1 million times, while the life of a traditional mechanical switch ranges from 100,000 to 200,000 times at most.
Volume and weight: The total thickness of a membrane switch is generally between 1.0 and 1.5 mm, with a small volume and light weight, which is only equivalent to the thickness of an ordinary aluminum panel.
Sealing: The membrane switch is a sealed structure of the whole machine, which has the ability to prevent fire, dust, explosion, and harmful gas erosion, and is particularly suitable for use in harsh environments.
Decorative: The appearance of the membrane switch is a diffuse matte color with a soft surface, which is beneficial to visual protection and more conducive to instrument monitoring. The appearance of a traditional mechanical switch is relatively simple.
Economical: The production of a membrane switch is completed once according to the design finalization, while a traditional mechanical switch requires complex processes and mold opening to complete, so a membrane switch has more advantages in production cost.
What are the applications of membrane switch?
The application of membrane switch is very extensive, covering multiple fields and equipment.
Electronic communication and electronic measuring instruments: membrane switches are used in electronic communication equipment, electronic measuring instruments, etc., with good waterproof, dustproof, oil-proof and other characteristics, and stable and reliable performance.
Industrial control: In the field of industrial control, membrane switches are used in various control panels to provide reliable switching operation.
Medical equipment: In medical equipment, membrane switches are used in various control switches to ensure the accuracy and reliability of operation.
Automotive industry: membrane switches are used in various control buttons and switches in the automotive industry, providing waterproof, dustproof and other functions.
Smart toys and household appliances: membrane switches are also widely used in smart toys and household appliances, such as remote controls, electronic locks, washing machines, microwave ovens, etc.
As a new type of electronic switch, membrane switch has the advantages of thin and beautiful appearance, good sealing, long life, good operating feel and low cost. As an important component of membrane switch, shrapnel also provides important guarantee for the performance and reliability of membrane switch.