What is Haptic Feedback?
Haptic feedback refers to the use of touch sensations to communicate with users. It often involves vibrations, motions, or forces applied to a device to simulate real-world interactions. This technology is commonly found in smartphones, gaming controllers, and automotive systems. By engaging the sense of touch, it enhances the user’s experience, making interactions more immersive and intuitive. For instance, the vibration felt when typing on a virtual keyboard is an example of haptic feedback.
Types of Haptic Feedback
There are different types of haptic feedback, each suited to specific applications:
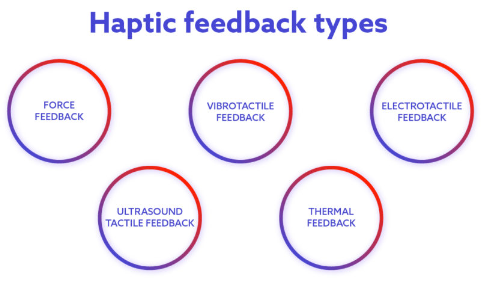
- Vibration Feedback: The most common type, found in phones and controllers. It uses motors to generate vibrations for alerts or immersive effects.
- Force Feedback: Found in devices like steering wheels for racing games. It simulates resistance or motion to create a realistic effect.
- Ultrasound Feedback: Uses sound waves to create touch-like sensations in mid-air. It’s often used in futuristic interfaces.
- Electrostatic Feedback: Alters surface friction on touchscreens to mimic texture. It’s used in advanced touch devices.
- Thermal Feedback: Changes temperature to simulate hot or cold sensations. It’s still in experimental stages but shows promise for VR applications.
What Are 5 Examples of Haptics?
Haptics appear in many everyday technologies. Here are five common examples:
- Smartphones: Vibrations for notifications and touch responses.
- Gaming Controllers: Force feedback for in-game interactions like crashes or shots.
- Wearable Devices: Fitness trackers using vibrations for alarms and activity reminders.
- Virtual Reality: Gloves or suits that simulate real-world sensations.
- Automotive Systems: Steering wheels vibrating to alert drivers about lane departures.

Is Haptic Feedback Good or Bad?
Haptic feedback offers numerous advantages but may also present some drawbacks depending on its implementation.
Advantages:
Improves user engagement by creating realistic interactions.
Enhances accessibility for visually impaired users by providing non-visual cues.
Increases safety, especially in cars, by delivering alerts without diverting attention.
Drawbacks:
Overuse of vibrations can feel distracting.
Poorly designed feedback may confuse users.
When implemented correctly, haptic feedback is highly beneficial and enhances the overall user experience.
What Is Tactile Feedback?
Tactile feedback involves the physical response users feel when interacting with a device. It’s commonly associated with buttons, keyboards, or touchscreens. Unlike haptic feedback, which may use vibrations or forces, tactile feedback provides a direct physical sensation, such as a button press.
The Benefit of Tactile Feedback
Tactile feedback offers several advantages:
- Clear Interaction Cues: Users receive immediate confirmation of their actions, reducing errors.
- Enhanced Precision: Physical sensations improve accuracy, especially in fast-paced tasks.
- Satisfying User Experience: The “click” of a button or keypress often feels more satisfying than virtual responses.
- Reliability in Various Conditions: Unlike haptic feedback, tactile responses don’t rely on power or software, making them dependable even in adverse conditions.
For many, the tangible nature of tactile feedback makes it indispensable in certain devices.
What Is the Difference Between Haptic and Tactile Feedback?
The primary difference lies in how the feedback is delivered. Haptic feedback relies on vibrations, forces, or motions to simulate touch sensations, often driven by technology. Tactile feedback, on the other hand, involves a direct physical response, such as the mechanical movement of a key or button. Here is a table shows their key differences in details.
| Aspect | Haptic Feedback | Tactile Feedback |
| Definition | Relies on vibrations, forces, or motions to simulate touch sensations. | Involves direct physical sensations, such as button clicks or key presses. |
| Mechanism | Uses electronic components like motors or actuators. | Involves mechanical or physical movements. |
| Versatility | Can mimic a wide range of sensations, including vibrations and forces. | Limited to physical interactions, like pressing a button. |
| Power Requirement | Requires electrical power to operate. | Doesn’t require power, as it’s purely mechanical. |
| Applications | Found in devices like smartphones, VR systems, and gaming controllers. | Used in keyboards, buttons, and touchscreens with overlays. |
| Feedback Type | Dynamic and programmable, adapting to various actions. | Static, providing a consistent mechanical response. |
| User Experience | Enhances immersion and accessibility through custom sensations. | Offers clarity and reliability in direct interactions. |
How to Improve the Tactile Feedback of Keyboards?
Improving tactile feedback in keyboards can significantly enhance typing comfort and efficiency. Here are some tips:
1. Choose Quality Switches: Mechanical keyboards with tactile switches offer precise feedback and a satisfying feel.
2. Optimize Actuation Force: Ensure the force needed to press keys aligns with user preferences. Lower force is better for speed, while higher force provides clarity.
3. Keycap Design: Textured or contoured keycaps enhance grip and typing accuracy.
4. Material Selection: Durable materials like PBT improve the feel and longevity of keyboards.
5. Adjust Actuation Force: Ensuring the right amount of force is required improves the typing experience.
6. Custom Keycaps: Using textured or specialized keycaps adds to the tactile feel.
7. Regular Maintenance: Cleaning and lubricating switches can preserve their tactile properties over time.
FAQs
Q: What devices use haptic feedback the most?
A: Smartphones, gaming controllers, and wearable devices are the most common examples.
Q: Can tactile feedback be added to touchscreens?
A: Yes, through specialized overlays or mechanical systems beneath the screen.
Q: Why is haptic feedback important in gaming?
A: It enhances immersion by simulating realistic interactions, such as the feel of a weapon or vehicle.
Q: Are there any health concerns with haptic feedback?
A: Overuse may cause mild discomfort, but it’s generally safe with proper design.
Q: What’s the future of haptics?
A: Advanced technologies like ultrasound and electroactive polymers are paving the way for more immersive experiences.